HERMES Initiative
Human Encounter Research for Measuring Exposure and Social mixing:
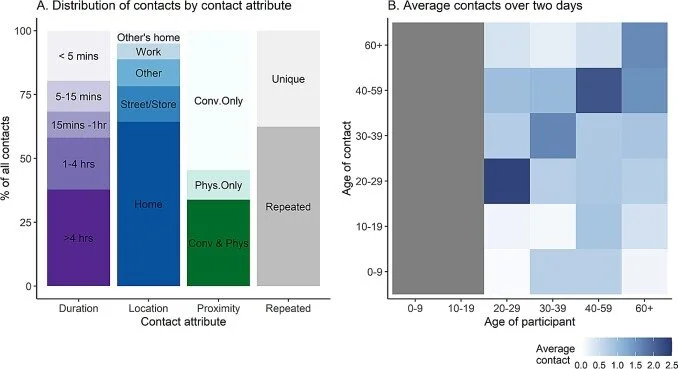
Mathematical models of infectious diseases inform public health policy and investment strategies of funding agencies. Data on social mixing patterns are a critical parameter for the development of realistic mathematical models that simulate disease transmission dynamics. Specifically, the rate at which people interact and the pattern of mixing (for example, between age groups) are fundamental parameters. They are critical to calculating who acquires infection from whom and the rate that people get infected. The HERMES initiative currently includes three studies -- GlobalMix, CorporateMix and Nursing Home Mix -- that are collecting these data from different populations.
Recent Papers
Nationally representative social contact patterns among U.S. adults, August 2020-April 2021
Nelson et al, Epidemics 2022
Rapid Review of Social Contact Patterns During the COVID-19 Pandemic
Liu et al, Epidemiology 2021
Kiti et al. Epidemics 2021
Rapid review of social contact patterns during the COVID-19 pandemic
Liu et at. Epidemiology 2021